Exploring the World of Interior Architecture
Delve into the realm of interior architecture, where design meets construction in a harmonious blend of creativity and functionality. From defining the key elements to understanding the historical influences, this topic offers a fascinating journey through the art of shaping interior spaces.
Definition of Interior Architecture

Interior architecture refers to the design and construction of interior spaces, focusing on the functionality, safety, and aesthetics of a space. It involves the manipulation of spatial volume, surface treatment, lighting, and furnishings to create an environment that meets the needs of the occupants.
Differences Between Interior Design and Interior Architecture
Interior design primarily deals with the decorative aspects of a space, such as color schemes, furniture selection, and accessories. On the other hand, interior architecture goes beyond decoration to address the structural elements of a space, including layout, circulation, and building systems integration.
Examples of Interior Architecture Influence
- Space Optimization: Interior architecture can optimize space by reconfiguring layouts, adding multifunctional elements, and maximizing natural light to create a more efficient and comfortable environment.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials in interior architecture can impact both the aesthetics and functionality of a space. For example, using sound-absorbing materials can improve acoustics in a room.
- Environmental Considerations: Interior architecture can incorporate sustainable design principles, such as energy-efficient lighting, natural ventilation, and eco-friendly materials, to create healthier and more environmentally friendly spaces.
Elements of Interior Architecture
Interior architecture encompasses various key elements that define the design and functionality of interior spaces. These elements include spatial organization, materials, lighting, color, texture, patterns, furniture layout, and circulation. Each element plays a crucial role in creating a cohesive and visually appealing interior design.
Spatial Organization
Spatial organization refers to how the different areas within a space are arranged and connected to each other. It involves the layout of rooms, corridors, and circulation paths to ensure efficient use of space and a smooth flow between areas.
Materials and Lighting
The selection of materials such as wood, glass, metal, and fabric can greatly impact the overall look and feel of a space. Similarly, lighting plays a significant role in highlighting architectural features, creating ambiance, and enhancing the functionality of a space.
Color, Texture, and Patterns
Color, texture, and patterns are essential elements in interior architecture as they can influence the mood, perception, and style of a space. The strategic use of these elements can help to define focal points, create visual interest, and establish a cohesive design scheme.
Furniture Layout and Circulation
Furniture layout and circulation are key considerations in interior architectural design as they impact the functionality and user experience of a space. The arrangement of furniture affects the flow of movement within a space, as well as the comfort and usability of the area.
Importance of Spatial Planning
Spatial planning plays a crucial role in interior architecture as it involves the organization and arrangement of spaces to create functional and visually appealing environments. It not only impacts the efficiency of a space but also influences the overall user experience.
Enhancing Functionality and Flow
Effective spatial planning ensures that the layout of a space is optimized to accommodate the activities and needs of its users. By strategically arranging furniture, fixtures, and circulation paths, interior architects can create efficient and ergonomic spaces that promote productivity and comfort.
For example, in an office setting, spatial planning can involve placing workstations in close proximity to shared amenities like meeting rooms and break areas to facilitate collaboration and communication among employees.
Creating Visual Hierarchy and Focal Points
Spatial planning also contributes to the aesthetic appeal of a space by establishing visual hierarchy and focal points. Through the careful arrangement of architectural elements, furniture, and lighting, interior architects can guide the eye towards key features or areas within a space.
This technique can be seen in the design of a living room, where a fireplace or a statement piece of furniture serves as a focal point, drawing attention and creating a sense of balance and harmony in the room.
Maximizing Space Utilization
Innovative spatial planning techniques like modular furniture systems, multifunctional design elements, and flexible room configurations allow interior architects to maximize the utilization of space. By incorporating elements that can adapt to different functions or be reconfigured as needed, designers can create versatile environments that can easily accommodate changing requirements.
For instance, in a small apartment, incorporating built-in storage solutions and foldable furniture can help optimize space and enhance the functionality of the living area.
Role of Technology in Interior Architecture
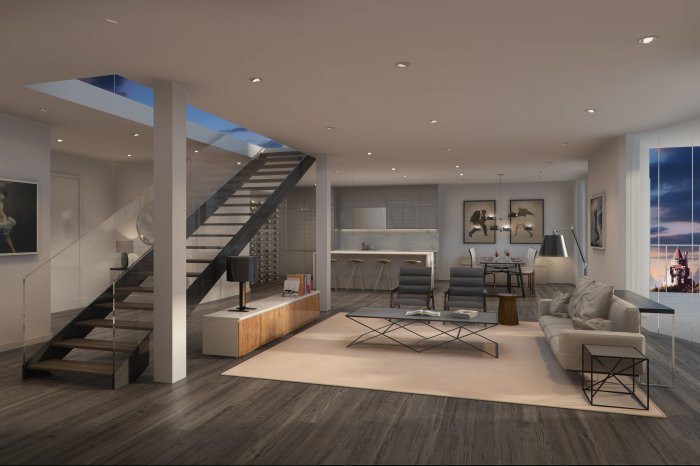

Technology has significantly impacted the field of interior architecture, revolutionizing design processes and enhancing the way designers create and visualize spaces. Advancements in technology have not only made the design process more efficient but have also led to the development of sustainable practices within interior architecture.
Use of Software Tools in Interior Architecture Designs
Software tools like AutoCAD, SketchUp, and Revit have become essential in the creation and visualization of interior architecture designs. These tools allow designers to create detailed 2D and 3D models, make real-time changes, and present their ideas to clients in a more immersive way.
Advancements in Technology and Sustainability
Technology has played a crucial role in promoting sustainability in interior architecture. With the use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, designers can analyze the environmental impact of their designs, optimize energy efficiency, and reduce waste during the construction process.
Additionally, the integration of smart technologies like IoT devices and energy-efficient lighting systems has further enhanced sustainable practices in interior architecture.
Historical Influences on Interior Architecture
Interior architecture has evolved significantly over different historical periods, reflecting the cultural movements and influences of each era. From ancient civilizations to modern times, interior architecture has been shaped by various factors that have left a lasting impact on design styles and trends.
Ancient Period
In ancient times, interior architecture was primarily focused on functional needs, with structures like the Egyptian pyramids and Roman villas showcasing grandeur and opulence. These spaces were adorned with intricate carvings, colorful frescoes, and luxurious materials, symbolizing power and wealth.
Medieval and Renaissance Period
During the medieval and Renaissance periods, interior architecture saw a shift towards more ornate and decorative styles. Gothic cathedrals and Renaissance palaces featured elaborate details, vaulted ceilings, and stained glass windows, reflecting religious and cultural influences of the time.
Baroque and Rococo Period
The Baroque and Rococo periods were characterized by lavish and extravagant interior designs, with palaces and churches embellished with intricate decorations, gilded accents, and elaborate furniture. These styles reflected the opulence and grandeur of the aristocracy and royalty.
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in interior architecture, with a focus on functionality, efficiency, and mass production. Factories, warehouses, and urban dwellings featured exposed structural elements, large windows, and open floor plans, reflecting the influence of industrialization on design.
Modern and Contemporary Period
In the modern and contemporary era, interior architecture has embraced minimalism, sustainability, and technological advancements. Spaces are designed to be sleek, efficient, and environmentally friendly, with a focus on clean lines, open spaces, and smart technologies that enhance the overall living experience.Iconic examples of interior architecture from different historical eras include the Palace of Versailles in France (Baroque), the Parthenon in Greece (Ancient), Fallingwater House by Frank Lloyd Wright (Modern), and the Guggenheim Museum in New York (Contemporary).
These structures showcase the diverse influences and styles that have shaped interior architecture throughout history.
Sustainable Practices in Interior Architecture
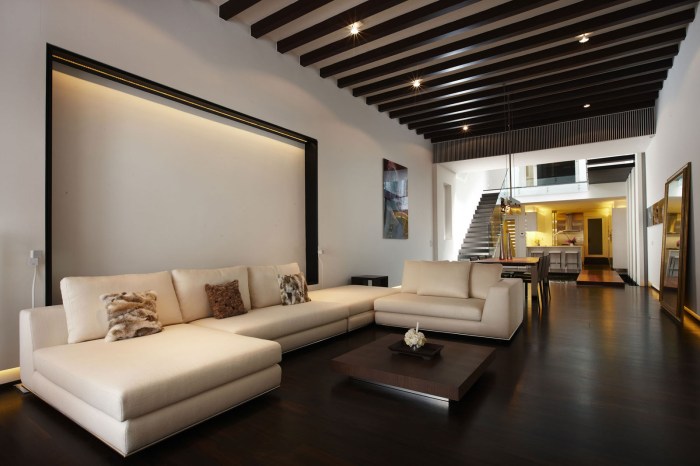

Sustainability in interior architecture is crucial for creating spaces that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially responsible. By incorporating sustainable practices, interior architects can reduce the negative impact on the environment, conserve resources, and promote the well-being of occupants.
Importance of Sustainable Materials
Using sustainable materials such as reclaimed wood, bamboo, recycled glass, and low-VOC paints can help reduce the carbon footprint of interior architecture projects. These materials are eco-friendly, durable, and contribute to a healthier indoor environment.
Energy-Efficient Systems
- Implementing energy-efficient lighting systems, HVAC systems, and appliances can significantly reduce energy consumption and operating costs in interior spaces.
- Utilizing natural light through strategic window placement and daylight harvesting techniques can also enhance the overall sustainability of a design.
Green Design Principles
- Integrating passive design strategies like natural ventilation, thermal mass, and shading devices can help minimize the need for mechanical heating and cooling.
- Incorporating green roofs, living walls, and rainwater harvesting systems can further enhance the sustainability of a project by reducing stormwater runoff and providing natural insulation.
Case Studies of Sustainable Projects
One notable example of sustainable interior architecture is the Bullitt Center in Seattle, which is designed to be a net-zero energy and water building. The use of solar panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and natural ventilation techniques makes the building highly sustainable and energy-efficient.
Ending Remarks
As we conclude our exploration of interior architecture, we reflect on the intricate balance between aesthetic appeal and practicality that defines this field. From spatial planning to sustainable practices, the world of interior architecture continues to evolve, shaping the way we experience our surroundings.
Question Bank
What is the difference between interior design and interior architecture?
Interior design focuses on the aesthetics and decorative elements of a space, while interior architecture deals with the structural aspects and spatial organization.
How does technology impact interior architectural design processes?
Technology has revolutionized interior architecture by streamlining design processes, offering advanced visualization tools, and enhancing sustainability practices.
Why is spatial planning important in interior architecture?
Spatial planning is crucial in optimizing the functionality and flow of a space, ensuring that it meets the needs of its occupants effectively.